The term "tenderness" in medical contexts carries significant importance in diagnosing various health conditions. It refers to the sensation of discomfort, pain, or soreness experienced when pressure is applied to a specific area of the body. Understanding tenderness medical meaning is crucial for healthcare professionals to identify underlying issues accurately and provide appropriate care.
Tenderness is not just a mere symptom but a vital clue in the diagnostic process. It can indicate inflammation, infection, injury, or other pathological conditions. By identifying the location, intensity, and nature of tenderness, doctors can narrow down potential diagnoses and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
This article delves into the comprehensive understanding of tenderness in medical practice, its significance, causes, assessment methods, and implications for patient care. Whether you're a healthcare professional, student, or someone curious about medical terminology, this guide will provide valuable insights into the tenderness medical meaning.
Read also:Exploring The World Of Movies A Comprehensive Guide For Enthusiasts
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Tenderness in Medicine
- Definition of Tenderness Medical Meaning
- Common Causes of Tenderness
- Types of Tenderness
- Diagnosing Tenderness
- Management and Treatment
- Preventive Measures
- Impact on Patient Care
- Latest Research on Tenderness
- Conclusion
Introduction to Tenderness in Medicine
Tenderness is a fundamental concept in the medical field, serving as a key indicator of various health conditions. It is often described as the sensation of pain or discomfort experienced when pressure is applied to a specific area of the body. This symptom can arise due to a wide range of factors, including injury, inflammation, or underlying diseases.
Importance in Diagnosis
In medical practice, tenderness plays a critical role in diagnosing ailments. It helps healthcare providers pinpoint the source of discomfort and identify potential underlying issues. By understanding the characteristics of tenderness, such as its location, intensity, and duration, doctors can make more informed decisions regarding treatment.
Scope of Application
Tenderness is relevant across various medical specialties, from orthopedics to internal medicine. Whether assessing a patient with abdominal pain or evaluating musculoskeletal injuries, tenderness serves as a valuable diagnostic tool. Its presence or absence can guide further investigations and interventions, ensuring timely and effective care.
Definition of Tenderness Medical Meaning
In medical terminology, tenderness refers to the sensation of pain or discomfort when pressure is applied to a specific area. This reaction is often a result of tissue irritation, inflammation, or nerve sensitivity. The tenderness medical meaning encompasses both subjective and objective components, as it involves the patient's experience and the clinician's assessment.
Subjective vs. Objective Tenderness
Subjective tenderness is reported by the patient, while objective tenderness is observed during a physical examination. Both aspects are essential for a comprehensive evaluation. For instance, a patient might describe localized tenderness in the lower abdomen, which the doctor can confirm through palpation.
Common Causes of Tenderness
Tenderness can stem from a variety of causes, ranging from minor injuries to severe medical conditions. Below are some of the most common causes:
Read also:Why Y Open Is Revolutionizing The Way We Unlock Opportunities
- Trauma: Bruises, sprains, or fractures often result in localized tenderness.
- Infection: Infections such as abscesses or cellulitis can cause significant tenderness in affected areas.
- Inflammation: Conditions like arthritis or tendonitis lead to tenderness due to inflammation.
- Neuropathy: Nerve-related issues can cause hypersensitivity and tenderness in certain regions.
Specific Conditions
Certain medical conditions are strongly associated with tenderness. For example, appendicitis often presents with tenderness in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen, while costochondritis causes chest wall tenderness. Recognizing these patterns helps in accurate diagnosis.
Types of Tenderness
Tenderness can be categorized based on its characteristics and underlying causes. Understanding these types aids in differentiating between various medical conditions.
Localized vs. Generalized Tenderness
Localized tenderness occurs in a specific area, such as a joint or muscle group. In contrast, generalized tenderness affects broader regions of the body and may indicate systemic issues like fibromyalgia or lupus.
Deep vs. Superficial Tenderness
Deep tenderness involves structures beneath the skin, such as bones or internal organs. Superficial tenderness, on the other hand, affects the skin and underlying tissues. This distinction is crucial for determining the depth and nature of the underlying problem.
Diagnosing Tenderness
The process of diagnosing tenderness involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Each step provides valuable information to guide the diagnostic process.
Physical Examination Techniques
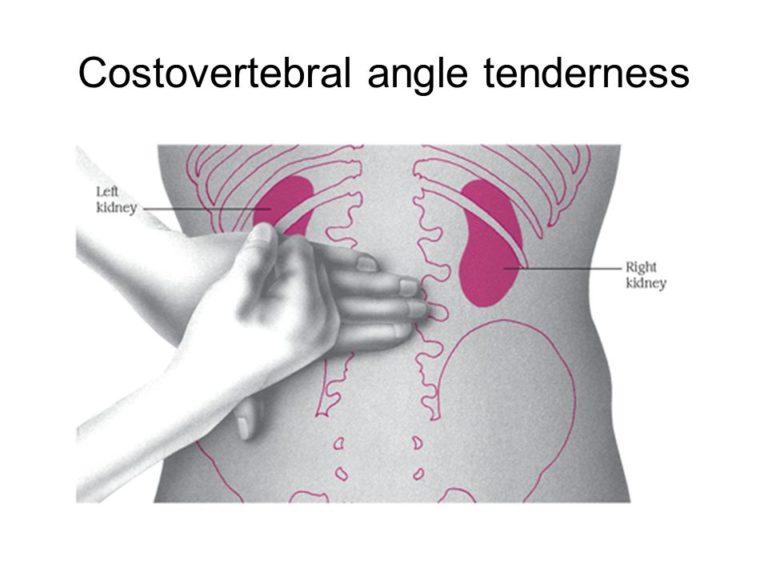
Healthcare providers use various techniques to assess tenderness. Palpation, percussion, and range-of-motion tests are commonly employed to evaluate the affected area. For example, palpating the abdomen can reveal tenderness indicative of gastrointestinal issues.
Diagnostic Tests
In some cases, additional tests are necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Imaging studies like X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs can help visualize internal structures and identify abnormalities. Blood tests may also be conducted to detect markers of inflammation or infection.
Management and Treatment
Managing tenderness involves addressing both the symptom and its underlying cause. Treatment options vary depending on the specific condition and its severity.
Conservative Measures
For mild cases, conservative measures such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can alleviate tenderness. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen may also be recommended.
Medical Interventions
More severe cases may require medical interventions, including prescription medications, physical therapy, or surgical procedures. For example, antibiotics are prescribed for infections, while corticosteroids may be used for inflammatory conditions.
Preventive Measures
Preventing tenderness involves adopting healthy lifestyle practices and avoiding risk factors. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper ergonomics can reduce the likelihood of developing conditions associated with tenderness.
Educational Programs
Public health initiatives and educational programs play a vital role in raising awareness about tenderness prevention. By educating individuals about risk factors and preventive strategies, healthcare providers can promote overall well-being.
Impact on Patient Care
Tenderness significantly impacts patient care, influencing diagnostic accuracy and treatment effectiveness. Recognizing and addressing tenderness promptly can improve patient outcomes and enhance quality of life.
Enhancing Communication
Effective communication between patients and healthcare providers is crucial in managing tenderness. Encouraging patients to describe their symptoms accurately helps clinicians make more informed decisions.
Latest Research on Tenderness
Ongoing research continues to explore the mechanisms and implications of tenderness in medical practice. Advances in imaging technology and biomarker identification have improved diagnostic capabilities. Studies also focus on developing novel treatment approaches to alleviate tenderness and its associated conditions.
Emerging Trends
Personalized medicine and genetic testing are emerging trends in the field of tenderness research. These approaches aim to tailor treatments based on individual patient characteristics, enhancing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Conclusion
Tenderness medical meaning is a critical concept in healthcare, serving as a cornerstone for diagnosing and managing various medical conditions. By understanding its causes, types, and implications, healthcare providers can deliver more effective and patient-centered care.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into medical topics. Together, we can foster a community of learning and support in the pursuit of better health outcomes.