Lipids play a crucial role in various biological processes, and understanding their monomer for lipid is essential for comprehending their structure and function. Lipids are a diverse group of molecules that include fats, oils, waxes, and certain steroids. They are vital for energy storage, cell membrane formation, and signaling processes. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of lipids and explore their building blocks.
From a biochemical perspective, lipids are composed of smaller units known as monomers. These monomers combine to form complex structures that perform specific functions within living organisms. By studying the monomer for lipid, scientists can better understand how these molecules contribute to cellular processes and overall health.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the monomer for lipid, its role in lipid formation, and its significance in biological systems. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply curious about the science behind lipids, this guide will offer valuable insights and knowledge.
Read also:Telugu Movierulz Your Ultimate Guide To Telugu Movies
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Lipids
- What is a Monomer for Lipid?
- Types of Lipids
- Structure of Lipids
- Monomer for Lipid Examples
- Functions of Lipids
- Lipid Biosynthesis
- Lipid Metabolism
- Importance in Health
- Conclusion
Introduction to Lipids
Lipids are an essential class of biomolecules that are hydrophobic or amphiphilic in nature. They are primarily composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. Unlike carbohydrates and proteins, lipids are not polymers but are formed by the combination of smaller units, known as monomers for lipid. These molecules are vital for energy storage, membrane structure, and signaling in living organisms.
The diversity of lipids arises from the variation in their monomer composition and the way these monomers are linked together. Understanding the basic structure and function of lipids is crucial for fields such as biochemistry, medicine, and nutrition.
What is a Monomer for Lipid?
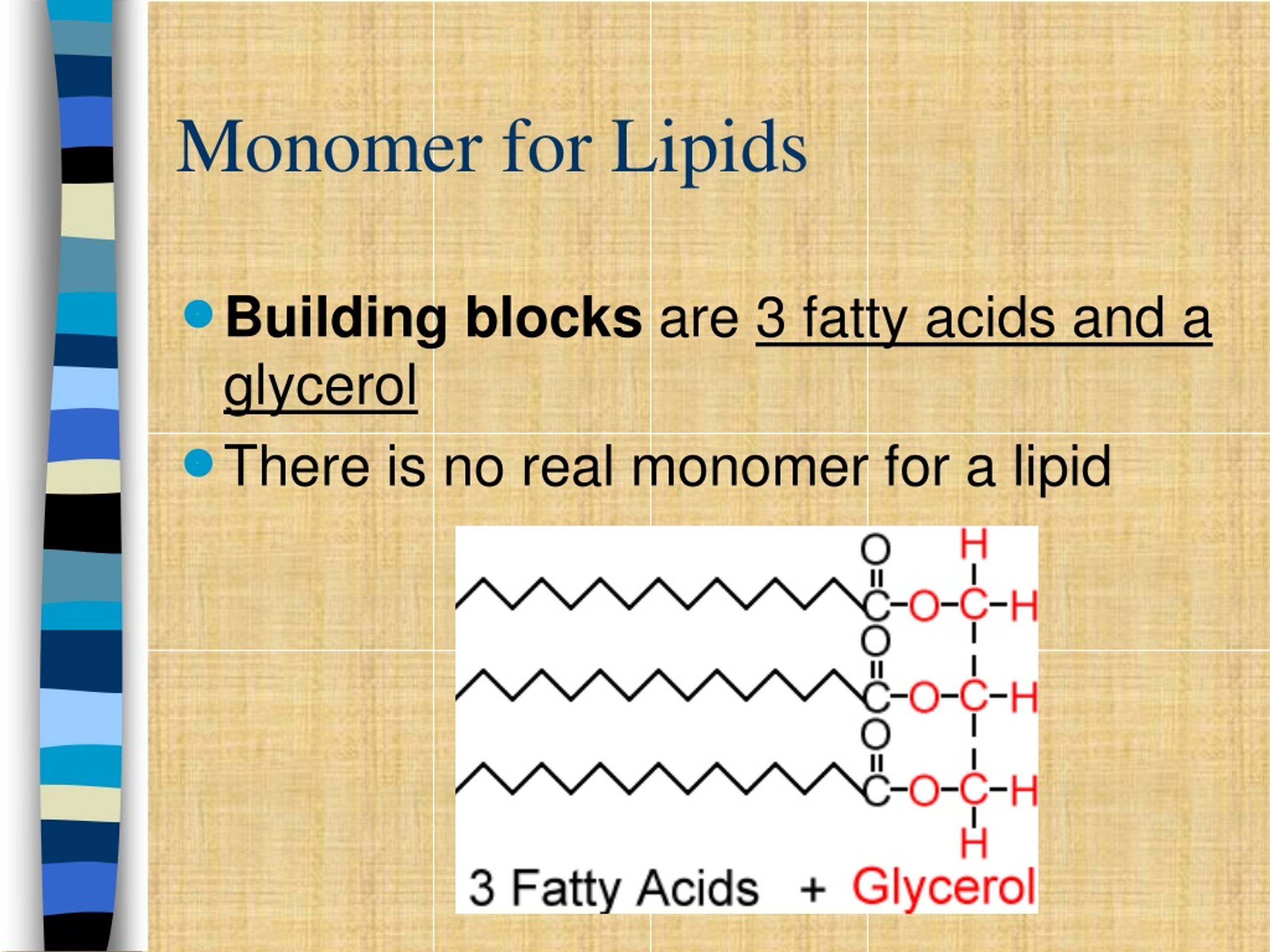
A monomer for lipid refers to the basic building block of lipids. In most cases, lipids are formed from glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol acts as a backbone, while fatty acids are attached to it through ester bonds. These fatty acids can vary in length and saturation, leading to the formation of different types of lipids.
Additionally, some lipids incorporate other molecules, such as phosphate groups or sugars, which further diversify their structure and function. The combination of these monomers results in complex lipids that play critical roles in biological systems.
Types of Lipids
Simple Lipids
Simple lipids, also known as triglycerides, are the most common type of lipid found in living organisms. They consist of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acids. Triglycerides are primarily used for energy storage and insulation in animals.
- Neutral fats: Composed of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
- Waxes: Contain long-chain fatty acids and alcohol groups.
Complex Lipids
Complex lipids are those that contain additional molecules, such as phosphate or sugar groups. These lipids are often involved in more specialized functions within the cell.
Read also:Indian Mms A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Exploring Its Impact
- Phospholipids: Key components of cell membranes.
- Glycolipids: Involved in cell recognition and signaling.
Structure of Lipids
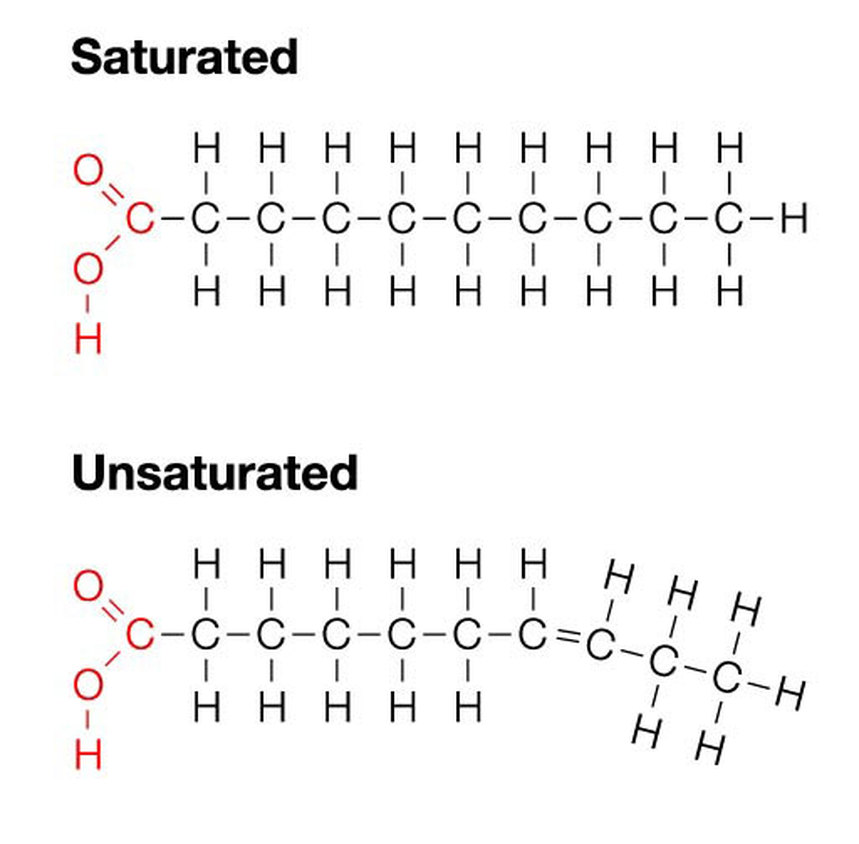
The structure of lipids is determined by their monomer composition. Glycerol serves as the central scaffold, with fatty acids attached to it through ester bonds. The fatty acids can vary in length, ranging from 12 to 24 carbon atoms, and can be saturated or unsaturated.
Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds between carbon atoms, making them more rigid and solid at room temperature. In contrast, unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more double bonds, which introduce kinks in their structure and make them liquid at room temperature.
Monomer for Lipid Examples
Here are some examples of monomers for lipid and their roles in lipid formation:
- Glycerol: Acts as the backbone for triglycerides and phospholipids.
- Fatty acids: Provide the hydrophobic chains that form the bulk of lipid molecules.
- Phosphate groups: Found in phospholipids, contributing to cell membrane structure.
- Sugars: Present in glycolipids, aiding in cell recognition and signaling.
Functions of Lipids
Lipids perform a wide range of functions in biological systems. Some of the key roles of lipids include:
- Energy storage: Triglycerides serve as a concentrated energy source.
- Membrane structure: Phospholipids form the bilayer of cell membranes.
- Signaling: Certain lipids act as signaling molecules, regulating cellular processes.
- Insulation: Lipids provide thermal insulation in animals.
Lipid Biosynthesis
Lipid biosynthesis is the process by which cells produce lipids from their monomers. This process involves several enzymatic steps and occurs primarily in the cytoplasm and endoplasmic reticulum. The synthesis of fatty acids begins with the formation of acetyl-CoA, which is then elongated and modified to produce fatty acids of varying lengths.
Glycerol is synthesized from glucose through glycolysis, and it combines with fatty acids to form triglycerides. Phospholipids are synthesized by adding phosphate groups to glycerol and fatty acids.
Lipid Metabolism
Lipid metabolism encompasses the processes of lipid breakdown and synthesis. Lipid breakdown, or lipolysis, involves the hydrolysis of triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids, which can then be used for energy production. This process is regulated by hormones such as insulin and glucagon.
In contrast, lipid synthesis, or lipogenesis, occurs when there is an excess of energy in the form of carbohydrates or proteins. The excess energy is converted into fatty acids and stored as triglycerides in adipose tissue.
Importance in Health
Lipids are vital for maintaining overall health and well-being. They provide energy, support cell structure, and regulate various physiological processes. However, an imbalance in lipid levels can lead to health issues such as obesity, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
Maintaining a balanced diet that includes healthy fats, such as omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, is crucial for optimal health. These essential fatty acids cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through the diet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the monomer for lipid is fundamental to comprehending the structure and function of lipids in biological systems. Lipids are composed of glycerol and fatty acids, which combine to form a diverse array of molecules with various roles in the body.
By studying the monomer for lipid and its role in lipid formation, researchers can gain insights into the mechanisms underlying lipid-related diseases and develop effective treatments. We encourage you to share this article and explore other resources to deepen your knowledge of lipids and their importance in health.
For further reading, we recommend consulting reputable sources such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and scientific journals like the Journal of Lipid Research.
![[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Monomer For Lipids](https://sciencetrends.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/aaace730-lipids.png)