Understanding the difference between ethnicity and race is crucial in today's diverse world. Many people use these terms interchangeably, but they carry distinct meanings. This article aims to clarify these differences and shed light on why these distinctions matter in social, cultural, and academic contexts.
As globalization continues to bring people from different backgrounds together, recognizing the nuances of identity becomes increasingly important. Ethnicity and race play significant roles in shaping individual and collective identities, influencing everything from personal experiences to societal structures.
This article will explore the definitions, historical contexts, and implications of both ethnicity and race. By the end, you'll have a clearer understanding of how these concepts differ and why it's essential to use them correctly in discussions about identity and diversity.
Read also:Is Emily Campano Married Discover The Truth Behind Her Personal Life
Table of Contents
- Definitions of Ethnicity and Race
- Historical Context of Ethnicity and Race
- Key Differences Between Ethnicity and Race
- Ethnicity and Cultural Identity
- Race from a Biological Perspective
- Social Implications of Ethnicity and Race
- Common Misconceptions About Ethnicity and Race
- Research Findings on Ethnicity and Race
- Global Perspective on Ethnicity and Race
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Definitions of Ethnicity and Race
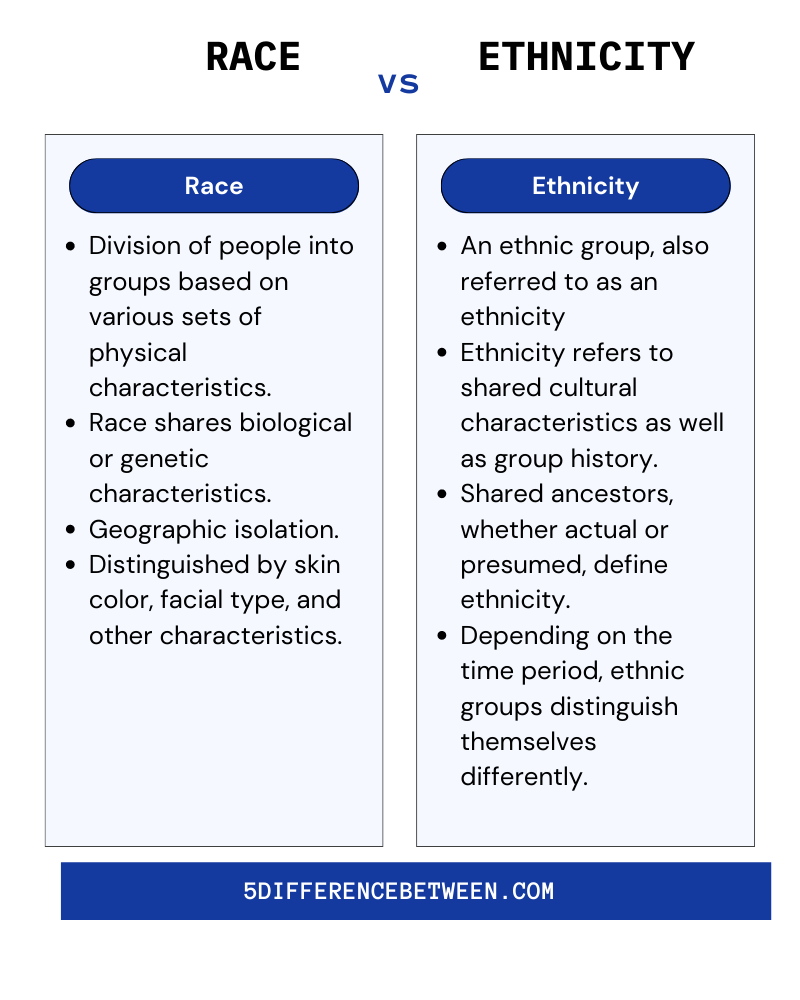
Before delving into the differences, it's essential to understand the basic definitions of ethnicity and race. Ethnicity refers to a group of people who share a common cultural heritage, including language, traditions, religion, and ancestry. On the other hand, race is a classification based on physical characteristics, such as skin color, facial features, and hair texture.
While ethnicity focuses on cultural identity, race is often tied to biological and physical traits. However, it's important to note that race is a socially constructed concept, and its definitions vary across different societies and historical periods.
Key Features of Ethnicity
Ethnicity encompasses a wide range of cultural elements that define a group's identity. These features include:
- Cultural practices and traditions
- Language and dialects
- Religious beliefs and rituals
- Shared history and ancestry
Historical Context of Ethnicity and Race
The concepts of ethnicity and race have evolved over time, shaped by historical events and societal changes. In ancient civilizations, people were often grouped based on their cultural practices and geographical locations. The modern understanding of race, however, emerged during the colonial era when European explorers categorized people based on physical differences.
Colonial Influences on Race
The transatlantic slave trade and colonialism played significant roles in solidifying racial hierarchies. These systems perpetuated the idea of racial superiority and inferiority, which continue to influence societal structures today.
According to historian Audrey Smedley, "Race was invented as a means of categorizing people for purposes of exploitation and control." This historical context highlights the importance of understanding race as a social construct rather than a biological reality.
Read also:Rachel Pizzolato The Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Key Differences Between Ethnicity and Race
Now that we've explored the definitions and historical context, let's examine the key differences between ethnicity and race. These distinctions are crucial for fostering meaningful discussions about identity and diversity.
- Ethnicity is based on cultural identity, while race is based on physical characteristics.
- Ethnicity can be self-identified, whereas race is often assigned by society.
- Ethnicity is fluid and can change over time, while race is typically seen as fixed.
Examples of Ethnicity and Race
To illustrate these differences, consider the following examples:
- Ethnicity: Italian, Irish, Nigerian, Indian
- Race: Black, White, Asian, Hispanic
Ethnicity and Cultural Identity
Ethnicity plays a vital role in shaping cultural identity. It influences how individuals perceive themselves and interact with others. People often take pride in their ethnic heritage, celebrating traditions, languages, and customs that have been passed down through generations.
Importance of Cultural Preservation
In an increasingly globalized world, preserving cultural identity becomes more challenging. However, maintaining ethnic traditions and practices is essential for cultural diversity and understanding. UNESCO emphasizes the importance of safeguarding intangible cultural heritage, recognizing its value in promoting peace and mutual respect.
Race from a Biological Perspective
From a biological standpoint, race lacks scientific validity as a means of categorizing humans. Genetic research has shown that there is more genetic variation within racial groups than between them. In fact, all humans share approximately 99.9% of their DNA, highlighting the arbitrary nature of racial distinctions.
Genetic Studies on Human Diversity
A study published in the journal Science revealed that genetic diversity is more closely linked to geographical ancestry than race. This finding challenges the traditional racial classifications and underscores the need for more nuanced discussions about human diversity.
Social Implications of Ethnicity and Race
The concepts of ethnicity and race have far-reaching social implications, influencing everything from personal relationships to public policy. Understanding these implications is essential for promoting equality and reducing discrimination.
Racial Discrimination and Its Impact
Racial discrimination remains a significant issue in many societies, affecting access to education, employment, and healthcare. Addressing these disparities requires acknowledging the historical and systemic factors that contribute to racial inequality.
Organizations like the United Nations and the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) work tirelessly to combat racial discrimination and advocate for equal rights for all individuals, regardless of their race or ethnicity.
Common Misconceptions About Ethnicity and Race
Despite growing awareness about the differences between ethnicity and race, many misconceptions persist. These misunderstandings can hinder efforts to promote inclusivity and understanding.
- Myth: Race is a scientific classification. Fact: Race is a social construct with no biological basis.
- Myth: Ethnicity and nationality are the same. Fact: Ethnicity refers to cultural identity, while nationality pertains to citizenship.
- Myth: Race determines intelligence or ability. Fact: There is no scientific evidence to support this claim.
Research Findings on Ethnicity and Race
Academic research has provided valuable insights into the complexities of ethnicity and race. Studies in sociology, anthropology, and genetics have challenged traditional notions and offered new perspectives on these concepts.
Interdisciplinary Approaches
Interdisciplinary research highlights the importance of considering multiple factors when examining ethnicity and race. For example, a study published in the Journal of Ethnic and Racial Studies explored how socioeconomic status intersects with race and ethnicity to shape life outcomes.
These findings emphasize the need for a holistic approach to understanding identity and diversity, recognizing the interconnectedness of various social and cultural factors.
Global Perspective on Ethnicity and Race
The global landscape of ethnicity and race is diverse and complex, reflecting the unique histories and cultures of different regions. While some countries have made significant progress in promoting equality and inclusivity, others continue to grapple with issues of discrimination and prejudice.
Case Studies from Around the World
Examining case studies from various countries provides valuable insights into the global dynamics of ethnicity and race. For instance, South Africa's post-apartheid efforts to address racial inequality offer lessons in reconciliation and social justice. Similarly, Canada's multicultural policies serve as a model for integrating diverse populations.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding the difference between ethnicity and race is essential for fostering a more inclusive and equitable society. By recognizing the cultural and social dimensions of these concepts, we can work towards reducing discrimination and promoting mutual respect.
We invite you to engage in this conversation by sharing your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our website to deepen your understanding of identity and diversity. Together, we can create a world where everyone feels valued and respected, regardless of their ethnicity or race.