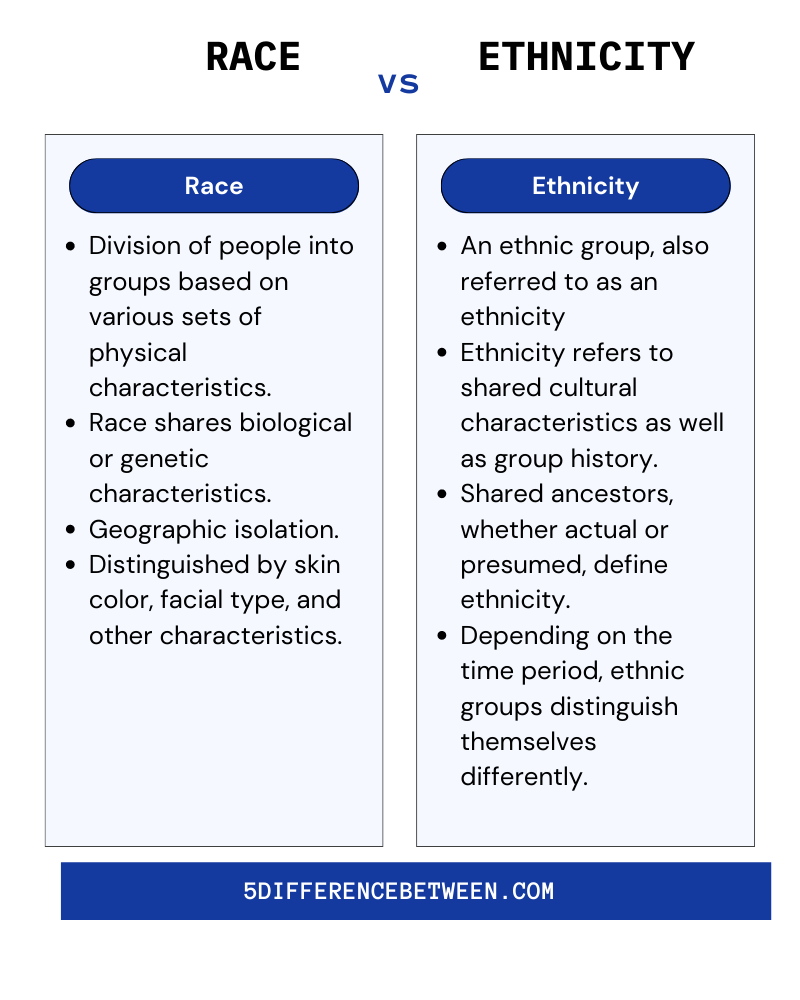
Understanding the difference between race and ethnicity is crucial in today's multicultural world. Both terms are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings that shape our identity and societal interactions. Race refers to physical characteristics and genetic traits, while ethnicity encompasses cultural, linguistic, and national affiliations.
As society becomes increasingly diverse, it is essential to grasp these distinctions to foster inclusivity and respect for individual backgrounds. Misunderstandings about race and ethnicity can lead to stereotypes and discrimination, making education on this topic more important than ever.
This article aims to clarify the definitions of race and ethnicity, explore their differences, and provide examples to deepen your understanding. By the end, you will have a clearer perspective on how these concepts influence personal and social dynamics.
Read also:Telugu Movierulz Your Ultimate Guide To Telugu Movies
Table of Contents
Key Differences Between Race and Ethnicity
Historical Perspective of Race and Ethnicity
Cultural Identity in Ethnicity
Read also:Is Emily Campano Married Discover The Truth Behind Her Personal Life
Societal Impacts of Race and Ethnicity
Examples of Race and Ethnicity in Real Life
Common Misconceptions About Race and Ethnicity
Definition of Race
Race is a classification system based on physical characteristics such as skin color, facial features, and hair texture. It is often rooted in biological and genetic traits that are inherited. While race is a social construct, it has significant implications in how individuals are perceived and treated in society.
For example, someone with dark skin may be categorized as belonging to the "Black" race, while someone with lighter skin might be considered "Caucasian." These classifications are not scientifically definitive but are widely used in social contexts.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, race categories include White, Black or African American, Asian, American Indian or Alaska Native, and Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander. These categories help collect demographic data but do not capture the complexity of individual identities.
Definition of Ethnicity
Ethnicity refers to a group's shared cultural heritage, including language, traditions, religion, and national origin. Unlike race, ethnicity is not based on physical appearance but on cultural and social factors. People of the same ethnicity may share common practices, values, and customs passed down through generations.
Key Elements of Ethnicity
- Language: The primary means of communication within an ethnic group.
- Traditions: Cultural practices, rituals, and celebrations unique to the group.
- Religion: Spiritual beliefs and practices that define the group's identity.
- National Origin: The country or region where the group's ancestors originated.
For instance, someone may identify as Hispanic based on their Spanish-speaking background and Latin American heritage, even if they belong to different racial groups.
Key Differences Between Race and Ethnicity
While race and ethnicity are interconnected, they serve different purposes in defining identity. Here are the main distinctions:
- Race focuses on physical attributes, whereas ethnicity emphasizes cultural affiliations.
- Race is generally assigned at birth based on appearance, while ethnicity is chosen or influenced by upbringing and environment.
- Racial categories are broader and less specific, while ethnic groups can be more nuanced and diverse.
Understanding these differences helps combat stereotypes and promotes a more inclusive worldview.
Historical Perspective of Race and Ethnicity
The concept of race emerged during the age of exploration and colonization, where European powers categorized people based on physical differences to justify exploitation and slavery. Ethnicity, on the other hand, has deep historical roots tied to migration, conquest, and cultural exchange.
Key Historical Events
- The transatlantic slave trade reinforced racial hierarchies, placing Europeans at the top and Africans at the bottom.
- Immigration waves in the 19th and 20th centuries brought diverse ethnic groups to the United States, leading to the melting pot metaphor.
- Modern civil rights movements have challenged racial and ethnic discrimination, advocating for equality and justice.
Today, historical biases continue to influence societal structures, underscoring the importance of education and awareness.
Genetic Factors in Race
Genetic research has shown that race is not a scientifically valid classification system. Human genetic variation is continuous and does not align with traditional racial categories. However, certain genetic traits, such as skin pigmentation and disease susceptibility, are more common in specific populations.
A study published in the journal Science found that genetic differences between individuals of the same race can be greater than those between different races. This highlights the complexity of genetic diversity and challenges simplistic racial categorizations.
Cultural Identity in Ethnicity
Ethnic identity plays a vital role in shaping an individual's sense of belonging and self-worth. It provides a framework for understanding one's place in the world and fosters connections with others who share similar backgrounds.
Examples of Ethnic Identity
- African Americans may celebrate their heritage through events like Kwanzaa and Juneteenth.
- Irish Americans may honor their ancestry by participating in St. Patrick's Day parades.
- Asian Americans may observe Lunar New Year traditions to connect with their cultural roots.
Embracing ethnic identity can lead to greater self-awareness and appreciation for diversity.
Societal Impacts of Race and Ethnicity
Race and ethnicity significantly influence social dynamics, affecting everything from employment opportunities to healthcare access. Discrimination based on race and ethnicity persists in many areas, creating barriers for marginalized groups.
Societal Challenges
- Racial profiling by law enforcement disproportionately affects minority communities.
- Ethnic stereotypes perpetuate harmful biases and limit individual potential.
- Systemic inequalities in education and economic resources perpetuate cycles of disadvantage.
Addressing these challenges requires collective action and policy changes to promote equity and justice.
Examples of Race and Ethnicity in Real Life
Real-world examples illustrate the complexities of race and ethnicity. Consider the following scenarios:
- A person of mixed-race heritage may struggle to identify with a single racial category, highlighting the fluidity of identity.
- An immigrant family may maintain their ethnic traditions while adapting to a new cultural environment, demonstrating the dynamic nature of identity formation.
- A community may come together to celebrate diversity through festivals and events, showcasing the richness of multiculturalism.
These examples underscore the importance of recognizing and respecting individual differences.
Common Misconceptions About Race and Ethnicity
Several misconceptions about race and ethnicity persist, contributing to misunderstandings and conflict. Here are a few common myths:
- Race is biologically determined: As discussed earlier, race is a social construct rather than a scientific classification.
- Ethnicity is fixed: Ethnic identity can evolve over time as individuals adapt to new environments and experiences.
- One must choose between race and ethnicity: Many people embrace both aspects of their identity simultaneously.
Challenging these misconceptions is essential for fostering informed discussions and promoting inclusivity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the difference between race and ethnicity lies in their definitions and applications. Race focuses on physical characteristics, while ethnicity emphasizes cultural affiliations. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for navigating today's diverse society and combating discrimination.
We encourage you to reflect on your own identity and how it intersects with race and ethnicity. Share your thoughts in the comments below or explore other articles on our site to deepen your knowledge. Together, we can create a more inclusive and equitable world for all.