Understanding the differences between race and ethnicity is essential in today's globalized society. These concepts shape our identities, influence cultural interactions, and affect social structures. Yet, many people still struggle to differentiate between the two terms or fully grasp their implications. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of race and ethnicity, their differences, and the importance of acknowledging them in everyday life.
Race and ethnicity are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts with unique characteristics. While race refers to physical traits and genetic backgrounds, ethnicity focuses on cultural, linguistic, and national affiliations. By exploring these differences, we can foster greater understanding and inclusivity in our communities.
This article will delve into the definitions, historical contexts, and social implications of race and ethnicity. We will also examine how these concepts intersect with identity, policy, and global dynamics. Whether you're a student, professional, or simply someone interested in learning more, this guide will provide valuable insights into race and ethnicity difference.
Read also:Aditi Mistry Unveiling The Multifaceted Career Of A Rising Star
Table of Contents
- Definition of Race and Ethnicity
- Historical Context of Race and Ethnicity
- Key Differences Between Race and Ethnicity
- Race and Ethnicity in Identity Formation
- Cultural Dynamics and Ethnicity
- Impact of Race and Ethnicity on Policy
- Global Perspective on Race and Ethnicity
- Challenges in Understanding Race and Ethnicity
- Conclusion: Moving Forward
- Resources for Further Learning
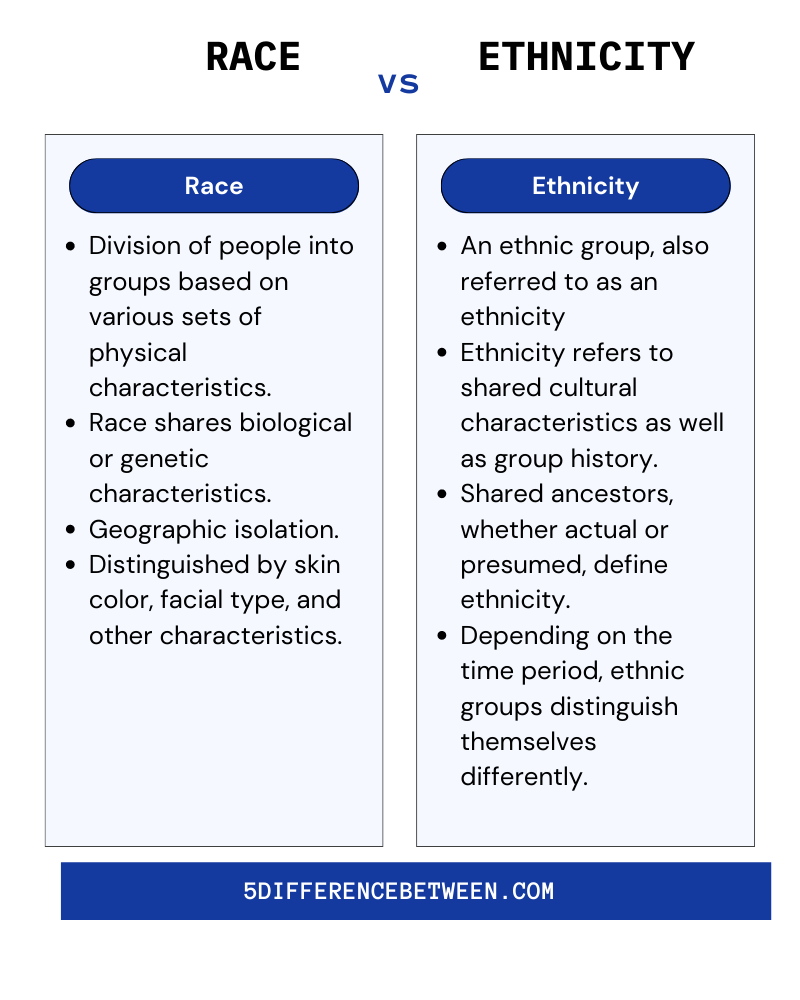
Definition of Race and Ethnicity
Race and ethnicity are foundational concepts in sociology and anthropology, yet they are often misunderstood. Race primarily refers to physical characteristics such as skin color, facial features, and genetic traits. It is a socially constructed category that has evolved over time to categorize people based on perceived biological differences.
Ethnicity, on the other hand, encompasses cultural, linguistic, and national affiliations. It reflects shared traditions, values, and practices that define a group's identity. While race is more about physical appearance, ethnicity is deeply rooted in cultural heritage and community ties.
Common Misconceptions
- Many people believe race is a fixed, biological concept, but it is largely a social construct.
- Ethnicity is sometimes reduced to food or music, ignoring its broader cultural and historical significance.
- Both race and ethnicity are dynamic and can change over time due to migration, assimilation, and globalization.
Historical Context of Race and Ethnicity
The history of race and ethnicity is deeply intertwined with colonialism, slavery, and imperialism. In the 18th and 19th centuries, European scientists and philosophers attempted to categorize human populations based on physical traits, leading to the development of racial hierarchies. These classifications were often used to justify exploitation and oppression.
Ethnicity, meanwhile, has been shaped by migration patterns, trade networks, and political boundaries. The formation of nation-states in the 19th and 20th centuries often prioritized specific ethnic groups, sometimes marginalizing others. This historical context continues to influence contemporary discussions about race and ethnicity.
Key Historical Events
- The transatlantic slave trade reinforced racial hierarchies and perpetuated systemic racism.
- Post-colonial movements emphasized ethnic identity as a means of resistance and empowerment.
- Globalization has led to increased cultural exchange and hybrid identities, challenging traditional notions of race and ethnicity.
Key Differences Between Race and Ethnicity
While race and ethnicity overlap in some areas, they differ fundamentally in their definitions and implications. Race is primarily based on physical characteristics, whereas ethnicity focuses on cultural affiliations. Understanding these differences is crucial for addressing social inequalities and promoting inclusivity.
For example, a person may identify as Black (race) and African American (ethnicity), highlighting the distinction between biological and cultural identity. These distinctions are not always clear-cut, as individuals may navigate multiple identities simultaneously.
Read also:Is Emily Campano Married Discover The Truth Behind Her Personal Life
Comparative Analysis
- Race: Defined by physical traits, often perceived as biological, and subject to social construction.
- Ethnicity: Defined by cultural practices, language, and heritage, emphasizing shared traditions and values.
Race and Ethnicity in Identity Formation
Identity is a complex and multifaceted concept influenced by race, ethnicity, gender, and other factors. For many individuals, race and ethnicity play a significant role in shaping how they see themselves and how others perceive them. This self-identification can vary depending on context, environment, and personal experiences.
In multicultural societies, individuals may navigate multiple identities, blending aspects of their racial and ethnic backgrounds. This hybrid identity challenges traditional notions of race and ethnicity, emphasizing the fluidity and adaptability of human identity.
Factors Influencing Identity
- Family and community values often shape early perceptions of race and ethnicity.
- Social interactions and media exposure can reinforce or challenge these perceptions.
- Globalization has expanded opportunities for cross-cultural exchange, influencing identity formation.
Cultural Dynamics and Ethnicity
Culture is a central component of ethnicity, encompassing language, traditions, food, and art. These cultural elements help define ethnic groups and create a sense of belonging among members. However, cultural dynamics are not static; they evolve over time in response to external influences and internal changes.
For example, the globalization of media has introduced new cultural elements to traditional ethnic groups, sometimes leading to tensions between preservation and adaptation. Balancing these forces is essential for maintaining cultural integrity while embracing modernity.
Examples of Cultural Preservation
- Language revitalization programs aim to preserve endangered languages and dialects.
- Traditional festivals and ceremonies celebrate ethnic heritage and foster community cohesion.
- Culinary traditions pass down cultural knowledge through generations, maintaining ethnic identity.
Impact of Race and Ethnicity on Policy
Policies related to race and ethnicity have significant implications for social justice, equality, and human rights. Affirmative action programs, for example, aim to address historical inequalities by promoting diversity in education and employment. However, these policies often face criticism and controversy, highlighting the complexities of addressing race and ethnicity in policy-making.
At the international level, human rights frameworks emphasize the importance of protecting ethnic minorities and combating racial discrimination. These efforts require collaboration between governments, organizations, and communities to ensure effective implementation.
Key Policy Areas
- Education: Promoting inclusive curricula that reflect diverse racial and ethnic perspectives.
- Employment: Ensuring equal opportunities for all individuals, regardless of race or ethnicity.
- Healthcare: Addressing disparities in access to healthcare services for marginalized groups.
Global Perspective on Race and Ethnicity
From a global perspective, race and ethnicity intersect with issues such as migration, nationalism, and human rights. The movement of people across borders has led to increased cultural diversity, but also challenges related to integration and identity. Nations must navigate these dynamics carefully to promote harmony and mutual respect.
International organizations like the United Nations play a crucial role in addressing these challenges by promoting dialogue, cooperation, and understanding. Their efforts focus on eliminating racial discrimination and protecting ethnic minorities, fostering a more inclusive global community.
Global Challenges
- Rising nationalism in some countries threatens ethnic minorities and promotes exclusionary policies.
- Refugee crises highlight the intersection of race, ethnicity, and humanitarian concerns.
- Technological advancements facilitate cross-cultural communication, but also amplify biases and stereotypes.
Challenges in Understanding Race and Ethnicity
Despite growing awareness, many challenges remain in understanding race and ethnicity. Stereotypes, biases, and misinformation continue to perpetuate misunderstandings and reinforce divisions. Education and open dialogue are essential for overcoming these barriers and fostering greater understanding.
Additionally, the fluidity of race and ethnicity poses challenges for research and policy-making. As identities evolve, it becomes increasingly difficult to categorize and analyze these concepts in meaningful ways. Embracing this complexity is key to advancing knowledge and promoting inclusivity.
Strategies for Improvement
- Encourage critical thinking and empathy in educational settings.
- Support research initiatives that explore the intersections of race, ethnicity, and identity.
- Promote inclusive policies that recognize and celebrate diversity.
Conclusion: Moving Forward
In conclusion, understanding the differences between race and ethnicity is vital for fostering inclusivity and addressing social inequalities. By recognizing the nuances of these concepts, we can promote greater awareness and respect for diverse identities. This article has explored the definitions, historical contexts, and implications of race and ethnicity, providing a foundation for further exploration.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Your voice matters in this ongoing conversation about race and ethnicity. Additionally, consider exploring other articles on our site to deepen your understanding of these important topics.
Resources for Further Learning
For those interested in learning more about race and ethnicity, the following resources provide valuable insights:
- United Nations: Promoting human rights and combating discrimination.
- American Anthropological Association: Advancing knowledge of race and ethnicity through research and advocacy.
- Human Rights Watch: Monitoring and addressing issues related to race, ethnicity, and human rights.